
- Download and install the software.
- It will scan your computer for problems.
- The tool will then fix the issues that were found.
Is your Windows 10/8/7 computer’s hard drive full for no reason, especially the E-drive? Is your computer running slow? Are you unable to save large files? Calm down! Here are some solutions to get you out of these problems. Read on to find what you need.
No doubt almost everyone has encountered the problem of a full disk under Windows 10/8/7. Many users have said, “my hard drive is full for no reason” or “my computer’s hard drive is full and I don’t know why.”
In general, as computer technology advances, hard drives are always filling up, even as they get bigger.
It may happen that the logical partition of the hard disk starts to fill up and quickly runs out. There may be several reasons for this. However, there are no special reasons for this behavior, there are several possible causes for this error. It could be due to malware, bloated WinSxS folder, sleeping settings, system corruption, system recovery, temporary files, other hidden files, etc.
Often, when the hard drive is full, only the electronic drive appears to be full. Many users address the “suddenly full electronic hard drive” problem in Windows 7/8/10. When your computer’s hard drive becomes full, you are likely to experience the following symptoms.
- Your computer runs slowly.
- You can no longer save large files/data on it.
- Your hard drive is not big enough to meet all your needs, such as software updates/updates, installing programs.
You may be wondering: why is my hard drive full under Windows 10/7/8? What is taking up space on my hard drive? Usually, it is because there is not enough space on your hard drive to store a lot of data.
Also, if you are only concerned about the “E-drive full” problem, it is likely that there are too many applications or files stored on it.
How do I fix this problem in Windows 10/7/8? Check out the solutions in the following sections right now.
Table of Contents:
What causes the local drive (E) to overflow in Windows 10?
If you get low-level notifications about your computer’s e-drive, which usually appears periodically on the desktop display or when you try to open the recovery drive, the drive may be full and you won’t be able to save any files to it.
The E drive is a recovery drive that you can use to store the files you need in a disaster recovery situation, such as when your system is unstable. It is a partition of your primary hard drive, taking up less free space than your local C: drive.
If you store files on Recovery Drive E, or if the backup program uses it to store files, it will fill up quickly, which can cause problems if you want to use the system recovery feature.
For this reason, you should not store any files in it other than those related to system recovery.
For optimal performance, Windows has set a limit of 200 MB. If your system falls below this limit, it automatically takes steps to maintain minimum performance.
When it drops below 80 MB, you will get a clear warning message as the system tries to free up space by deleting restore points.
However, if the available space drops below 50 MB, it will be saved and you will receive an urgent warning almost every four minutes, warning you that there is not enough space on the electronic hard drive until you free up space.
To make up for the lack of space on the e-warning device, there are several steps you can take to get some free space back.
First, you need to determine how much space the operating system has and what data or applications are taking up that space, and then decide what to delete or erase.
How to repair the local hard drive (E), which often seems to be overcrowded
Updated: April 2025
This tool is highly recommended to help you fix your error. Plus, this tool offers protection against file loss, malware, and hardware failures, and optimizes your device for maximum performance. If you already have a problem with your computer, this software can help you fix it and prevent other problems from recurring:
- Step 1 : Install the PC Repair and Optimizer Tool. (Windows 10, 8, 7, XP, Vista).
- Step 2 : Click Start Scan to determine what problems you are experiencing with your computer.
- Step 3 : Click Repair Allto resolve all problems.
Before you continue, make sure that your computer has an active Internet connection and that you have administrator rights. Start with the first solution and work your way down.
Solution 1: Change the driver letter
Windows has officially acknowledged the situation and has even released a workaround you can use to solve the problem. According to it, Windows Update creates this drive temporarily to store all update files and must delete it before the update process is completed and control is returned to the user. In our case, the update process doesn’t do that and instead leaves everything else behind.
According to Microsoft, the problem can be solved immediately by changing the drive letter in Disk Management. There are two ways to do this: either by the application itself or by the command line. In this solution we will look at both methods, starting with the GUI method.
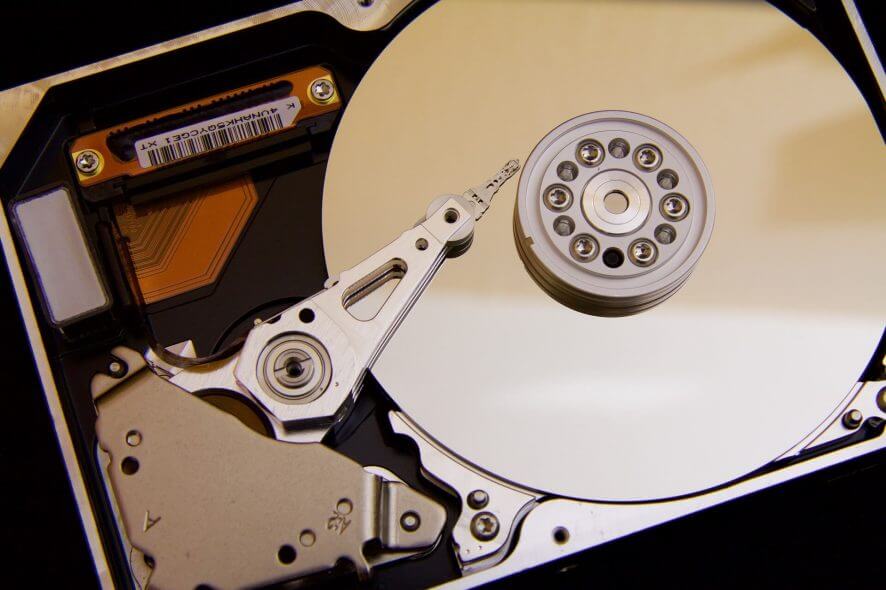
1.) Press Windows + R, in the dialog box type “diskmgmt.msc” and press Enter.
2.) While in the Disk Manager, locate the disk that happened to be after the upgrade. Right-click on it and choose “Change drive letters and paths“.
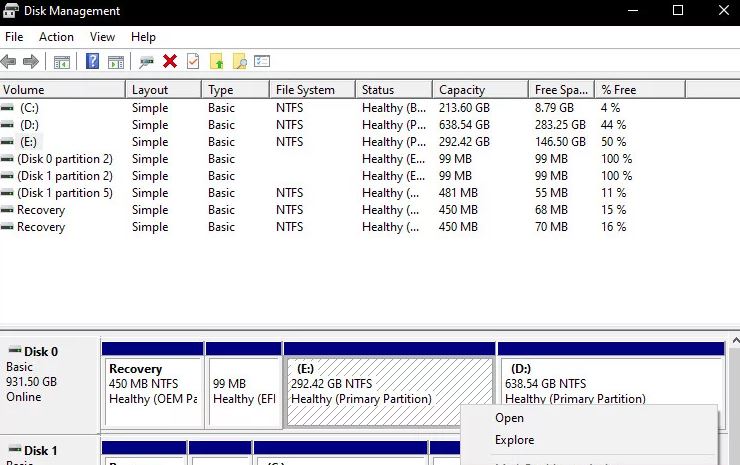
3.) Another small window should open with the drive name. Select the disk and click on the Delete button at the bottom.
4.) Now, after deleting it, restart your computer completely and check if the problem is resolved.
Another way to perform the same steps is with the command line. Follow the instructions below:
1.) Press Windows + S, type “Command Prompt” in the dialog box, and press Enter.
2.) While at the extended command prompt, run the following commands in order.
partition
selected E volume
delete letter=E
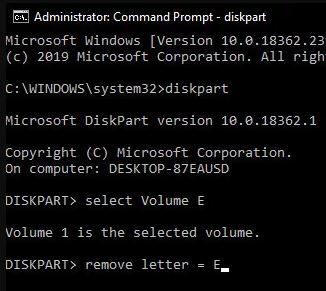
Note: In this case, the drive letter that accidentally appeared was “E”. If your case is different, you can change the command accordingly.
3.) Reboot your computer completely and then check if the problem persists.
Solution 2: Update Windows with the latest version
According to Microsoft, an update has been released for the computers affected by this problem, in which the problem has been fixed. In addition, update 1803 has also been modified so that the problem does not occur to users who are upgrading. In our case, the Windows update will automatically download a workaround to your computer and fix the problem completely. In this solution, we will go to settings and then update Windows to the latest version.
1.) Press Windows + S, type “Update” in the dialog box, and press Enter.
2.) While in Windows Update, click the “Check for updates” button.
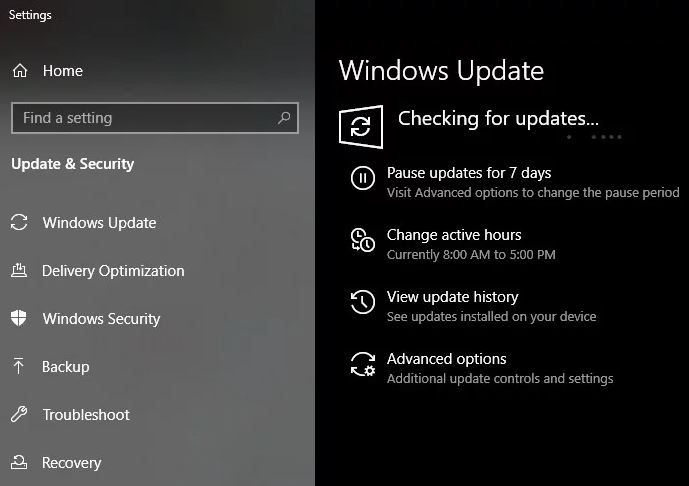
3.) Windows will now automatically connect to Microsoft’s servers and download the new version to your computer.
4.) When prompted, make sure your computer is completely rebooted, and then check to see if the new updates have solved the problem for you.
Solution 3: Check network drives
Another reason why you might see another drive on your computer is that it is mapped to your computer on the network. If you use another computer’s network access, its files will be on your computer, but under Network Locations. In this solution, we will go to “My Computer” and, after checking that the drive is a network location, we will remove it completely.
Note: After disconnecting the drive from the computer you will need to go through all the steps to reconnect it, so make sure you know what you are doing.
1.) Open “This PC” either from your desktop or from the Start menu.
2.) Now, look under “Network Attached Storage”. If the drive is present in this section, it means that it is shared on the network. If it is not, you can troubleshoot it.
3.) Now right-click on the drive and select “Disconnect”.
4.) This will disconnect the drive and remove it from the computer.
Another way to remove the disk is via the command line.
This method provides the same solution, but through the command line.
1.) Open the extended command line as in the previous solutions.
2.) Now run the following commands: net use E: /delete
Note: In this case, the drive to be extracted has the letter “E”. If your case is different, you must reverse the order.
Solution 4: Check for malicious or external hard drives
If both of the above methods do not work or are not applicable in your case, it probably means that your computer has an external hard drive/drive and it is visible. If it is an external drive, you can easily check if it is connected to your computer. Check all the connections.
If you can access the contents of the drive, but it wasn’t there before and you’re also using your computer, you need to make sure your computer didn’t have a malicious drive.
Check all the SATA ports and make sure there isn’t a drive that wasn’t there but is.
If there really was a faulty/external hard drive, sit back and enjoy. We hope that at the end of this article you have solved the problem.
APPROVED: To fix Windows errors, click here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is my local E drive full?
This problem is known to be caused by the Windows 10 v1803 update released by Microsoft in April, which assigned a letter to the system recovery partition. So, if you see a new partition in Windows Explorer, it's probably because of this and not because of malware.
What is a local E drive in Windows 10?
A local drive is a hard drive or SSD installed in or attached to your computer. It is not part of another computer on the network. A DVD-RW drive (E:) is a local drive, but is considered a removable drive. Any other network drive or cloud storage is a remote drive.
What happens when the local C drive is full?
When the space in the C drive is full, you should move unused data to another drive and remove installed applications that are not used often. You can also perform a disk cleanup to reduce unnecessary files on the drives, allowing your computer to run faster.
How do I empty my local E hard drive?
Clean up the drive.
To access it, right-click on one of the hard drives in your computer window and select Properties. (You can also simply search for "Clean Up Disks" on the Start menu.) In the hard drive's properties window, click on "Erase Disk". Select the types of files you want to delete and click OK.

